Legal Challenges to New Title IX Regulations Begin, Blocking Legal Protections for Gender Identity in Education
 Title IX, passed by Congress over fifty years ago as part of the Educational Amendments of 1972, begins with a deceptively simple sentence: “No person in the United States shall, on the basis of sex, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any education program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance.”
Title IX, passed by Congress over fifty years ago as part of the Educational Amendments of 1972, begins with a deceptively simple sentence: “No person in the United States shall, on the basis of sex, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any education program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance.”
Since 1972, the law has been interpreted by the courts, by the Department of Education (the agency charged with implementing the law), and the Department of Justice (responsible for Title IX enforcement in federal agencies). This April, the Biden administration finalized a long-awaited set of new regulations, which will replace those put in place in 2020 under President Trump. Among other provisions, the new regulations radically change the procedures for reporting and adjudicating allegations of sexual misconduct at colleges and universities. The new regulations also make clear that the term “sex” as used in Title IX includes sexual orientation and gender identity. Before the Biden regulations go into force in August, however, they are already coming under legal attack. In June, two federal district courts, one in Kentucky and one in Louisiana, issued preliminary injunctions blocking the enforcement of the new regulations in ten states: Idaho, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Montana, Ohio, Tennessee, Virginia, and West Virginia.
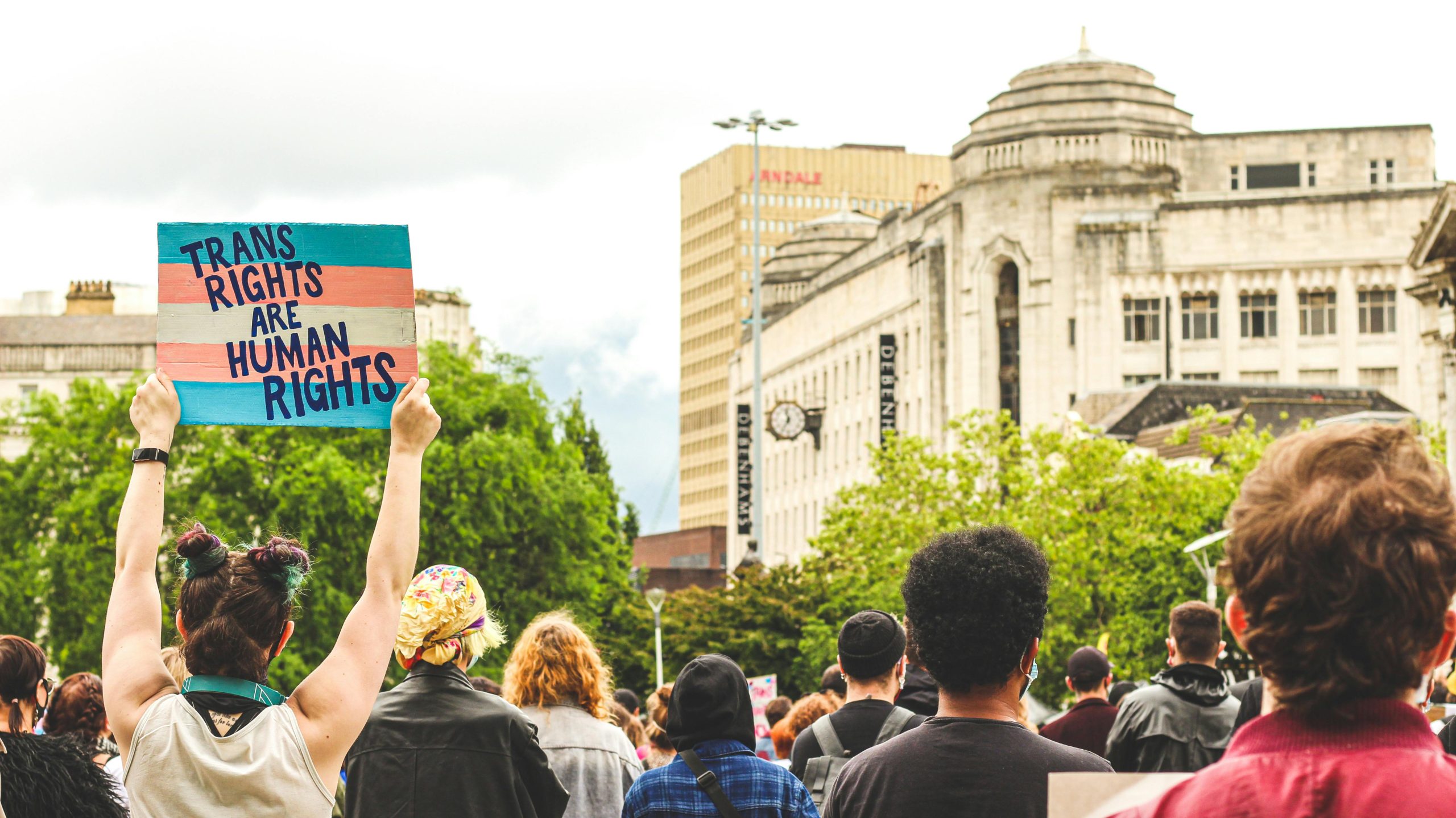
The plaintiffs included the affected states, plus an association of Christian teachers and a female student-athlete in the Kentucky case, and a group of local public schools boards in the Louisiana case. They primarily challenged the new regulations’ inclusion of discrimination based on gender identity within the ambit of discrimination “on the basis of sex,” with a view to its effects on primary and secondary education. Following the pattern of recent conservative attacks on trans and non-binary people, the plaintiffs objected to how the inclusion of gender identity would require public schools to allow students to use bathrooms and to play on sports teams associated with their gender identity, as well as potentially mandating that teachers and classmates use the pronouns used by a student themselves.
 Boston Lawyer Blog
Boston Lawyer Blog